Your Wall of Defense is Only as Strong as the Weakest Brick…We’ll Find it and Fix it.
The Pain Point:
Identify and Exploit Vulnerabilities
Penetration testing is a method to safely identify and exploit vulnerabilities in a company’s attack surface, including flaws in operating systems, services, applications, configurations, and end-user behavior. In addition, it can validate defensive mechanisms and ensure compliance with security policies to help make strategic conclusions and prioritize remediation efforts.
The Remedy:
Camelot Has the Experience
Experience makes a difference!
Camelot’s Offensive Security (COS) Team is trusted because we offer experienced and qualified professionals who deeply understand cybersecurity best practices and the latest threat trends. In addition, we have decades of experience testing IT security infrastructures and millions of devices. All this knowledge allows us to:
Provide a better understanding of different attack methods and identify vulnerabilities inexperienced testers may miss.
Simulate real-world attack scenarios more likely to occur in the most recent cybersecurity landscape.
Take the necessary precautions to prevent causing damage or disruption to business operations while performing a penetration test.
Camelot’s Penetration Test Difference
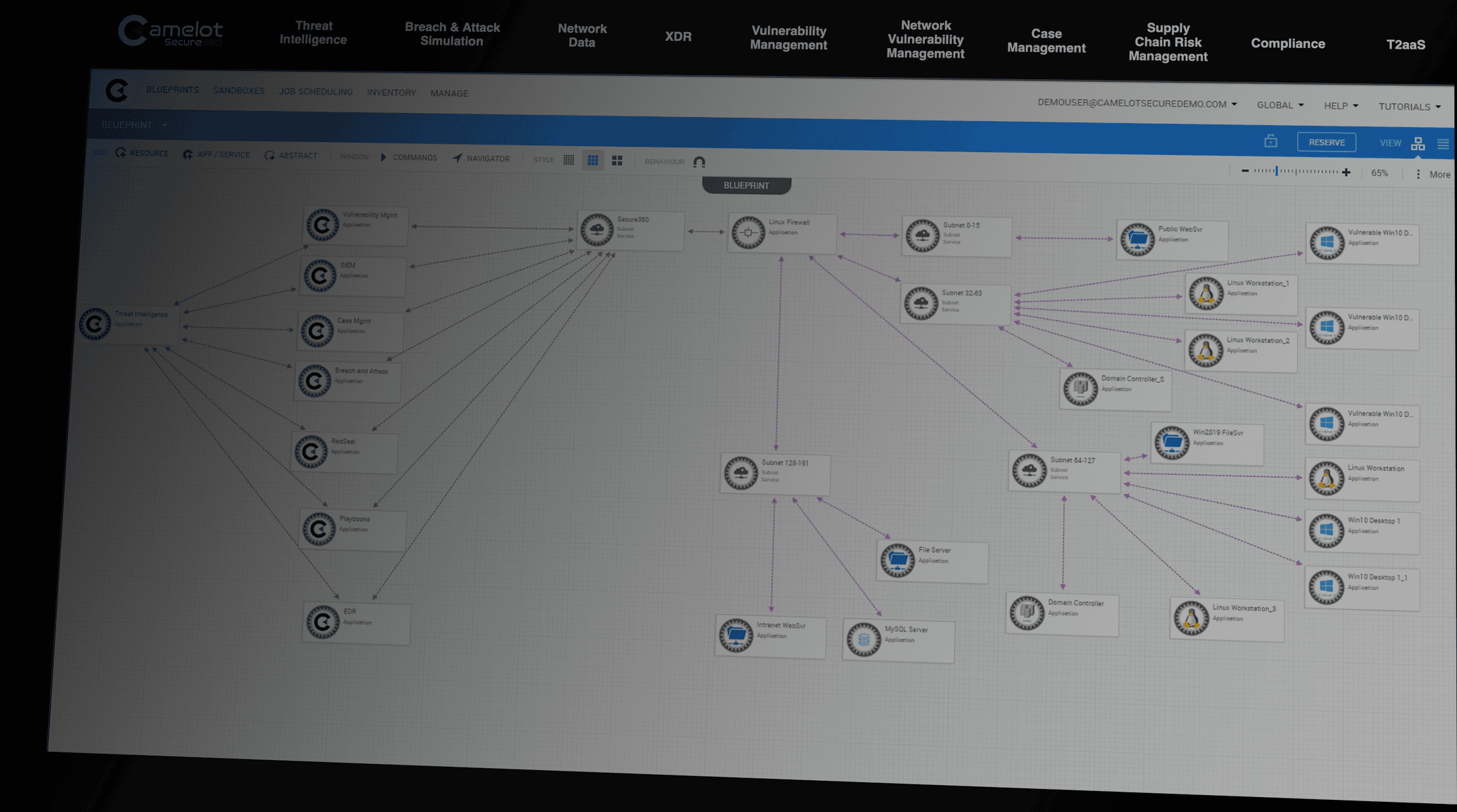
Camelot has developed a revolutionary offensive security platform that has been meticulously designed to manage and scrutinize the publicly accessible assets and network infrastructure of any company.
Unlike companies that rely on manual penetration testing and require more information, Camelot leverages Artificial Intelligence (AI) to enhance its capabilities.
By automating the penetration test process, AI enables Camelot to promptly produce an accurate representation of over a million devices and expose information that would typically remain hidden during manual reviews.
Our Red Team AI model and automated processes provides unparalleled security scanning capabilities
Full-Scope IT Systems Penetration Testing
As part of Camelot’s penetration testing services, we incorporate an attack surface management feature to assist organizations in detecting potential weaknesses in their networks and systems. Revealing weaknesses is achieved by consistently monitoring targets, services, IPS, domains, networks, hostnames, and other artifacts that attackers typically observe when targeting an organization.
The IBM Security X-Force Threat Intelligence Index 2023 study found, “The time to execute attacks dropped 94% over the last few years. What took months now takes attackers mere days.”
These security scanning capabilities are unique among penetration testing capabilities because they produce comprehensive threat intelligence, predict attack patterns, and devise customized attacks that adjust to the specific data of your environment.
▪ Automated asset discovery, content gathering
▪ Vulnerability scanning continuously discover and monitor all IT assets.
▪ Vulnerability scanning continuously discover and monitor all IT assets.
- Forecast attack progressions.
- Custom-tailor attacks that adapt to your specific network.
- Analyze security scan data.
- Generate precise threat intelligence.
- Predict attack progressions.
- Devise attacks based on unique environmental factors.
Camelot offers 3 Types of Testing Methods: External, Internal, and Web
The IBM Security X-Force Threat Intelligence Index 2023 states, “Phishing was the leading infection vector, identified in 41% of incidents. More than half of phishing attacks used spear-phishing attachments. X-Force also observed a 100% increase in thread hijacking attempts per month—where an attacker impersonates someone and uses existing email conversations for nefarious purposes.”
External
Counterintelligence assessment – Counterintelligence is a risk assessment technique that evaluates the likelihood of harmful activities like espionage or sabotage. It entails gathering and scrutinizing information from legally accessible and publicly available sources, such as social media posts, news articles, and public records. Camelot employs this approach to identify possible security threats or vulnerabilities to an organization, enabling them to proactively implement measures to mitigate the risks of security incidents like cyber-attacks or data breaches.
Social engineering assessment – Social Engineering attacks rely on manipulating or tricking individuals into revealing sensitive information or carrying out actions that could compromise an organization’s security. Camelot offers a range of tactics, such as phishing attacks, pretexting, and baiting, to identify employees who might inadvertently execute such an attack.
Internal
Internal penetration test – Often called an “Evil Janitor,” this type of penetration test simulates someone with physical access to a client’s facility and the ability to connect a device to their network. The test is designed to identify ports and services that a threat actor could use to gain unauthorized access to systems within the target’s internal domain.
Physical security and access penetration test – This test evaluates an organization’s defenses against physical attacks on its premises, facilities, and assets. Techniques used in this assessment include piggybacking, lock picking, impersonation, badge cloning, and hacking surveillance systems to gain unauthorized access to an organization’s facility.
Assumed breach penetration test – This assessment integrates elements of penetration testing and Red Teaming and operates assuming that an organization’s defenses have been breached. It concentrates on ascertaining the extent of the compromise and the actions an attacker could undertake once they have obtained access. The assessment utilizes techniques such as escalating privileges, exfiltrating data, and laterally navigating the network to gain entry to other systems and resources.
Web
- Web application test – Designed to uncover vulnerabilities in an organization’s web application defenses. This test includes identifying weaknesses in the application’s code, evaluating the effectiveness of security controls such as firewalls and intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and assessing the application’s overall security posture. It employs techniques and tools to test the application’s security, such as identifying and exploiting vulnerabilities like SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS). Additionally, it assesses the application’s resilience against various types of attacks, including denial of service (DoS) attacks and session hijacking.
The 360 Response:
Camelot’s Process from Information Gathering to Full Reporting – in just 4 Days
- Clearly define the rules of engagement, including systems and networks to test and any exclusions or limitations.
- Develop a plan for testing, and define timelines and outcomes.
- Develop a plan for testing and obtain approval from the client.
- Obtain necessary permissions from the client and relevant third parties.
- Conduct testing and engage with the client throughout the process.
- Prepare reports that outline vulnerabilities and provide remediation recommendations.
- Work with the client to adequately address identified vulnerabilities to secure their systems and networks.
